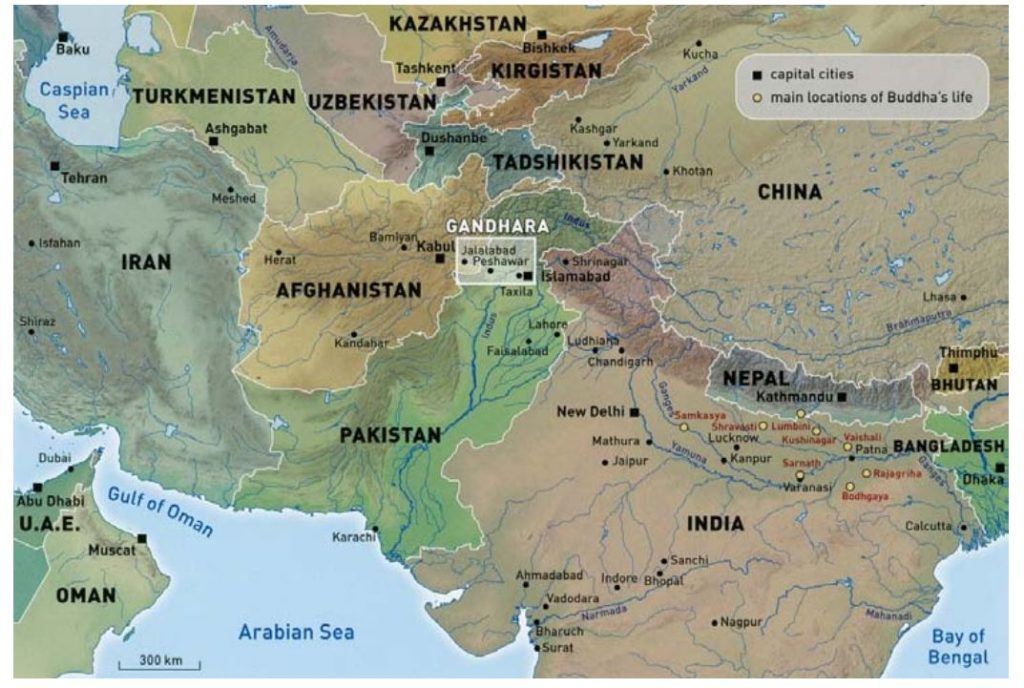
Gandhara គឺជាឈ្មោះរដ្ឋបុរាណ និងអរិយធម៌ដ៏ល្បីល្បាញមួយដែលបច្ចុប្បន្នស្ថិតនៅភាគពាយ័ព្យនៃប្រទេសប៉ាគីស្ថាន និងអាហ្វហ្គានីស្ថាន ហើយមានព្រំប្រទល់ខាងលិចជាប់នឹងជួរភ្នំគ្រុស និងខាងជើងជាប់នឹងជើងភ្នំហិម៉ាល័យ។ តាមរយៈសំណង់ស្ថាបត្យកម្ម សំណល់បុរាណវិទ្យា និងជាពិសេស វត្ថុសិល្បៈ នៃ Gandhara មានអាយុលកាលប្រមាណជាង២០០០ឆ្នាំ។
ប្រភព៖ Falser
Gandhara គឺជាតំបន់គោរពប្រតិបត្តិព្រះពុទ្ធសាសនា ប៉ុន្តែក្រោយមកនៅឆ្នាំ៣៣០ មុនគ.ស. Alexander the great បានគ្រប់គ្រងលើតំបន់Gandharaនេះ ហើយឥទ្ធិពលនៃអរិយធម៌ក្រិចក៏បានជ្រៀបចូលក្នុងតំបន់នេះយ៉ាងខ្លាំង ដោយបានបង្កើតទៅជាសិល្បៈ និងវប្បធម៌មួយដែលហៅថា Greco-Buddhist ឬ Indo-Greek (ពុទ្ធសាសនាបែបក្រិច)។

ប្រភព៖https://www.guimet.fr
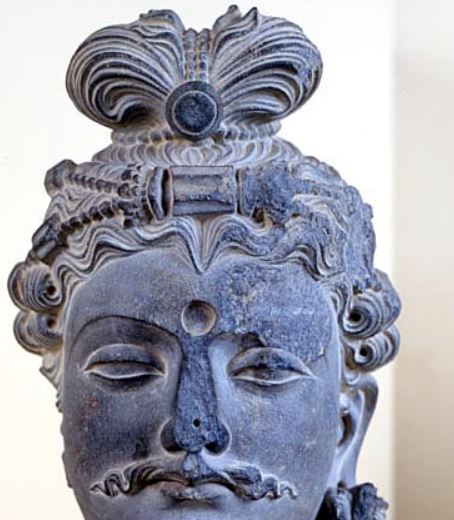
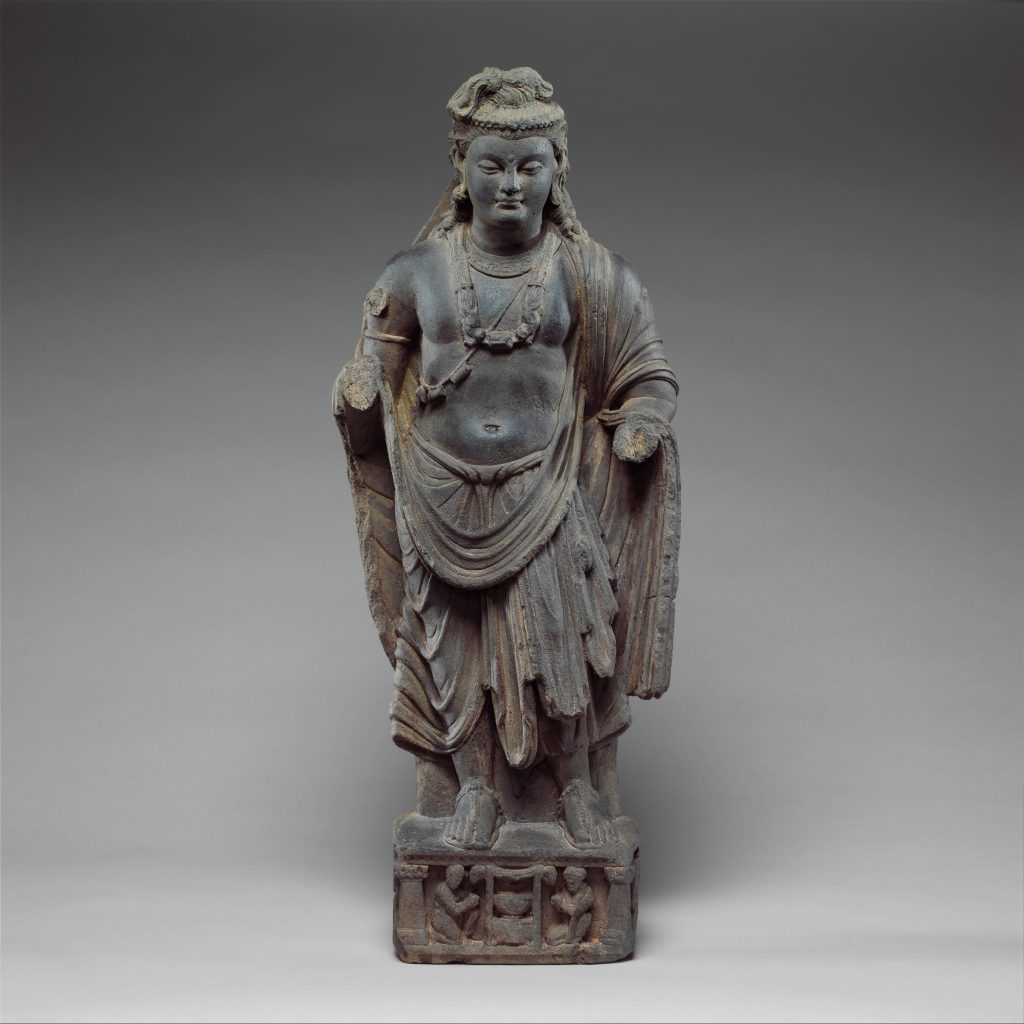
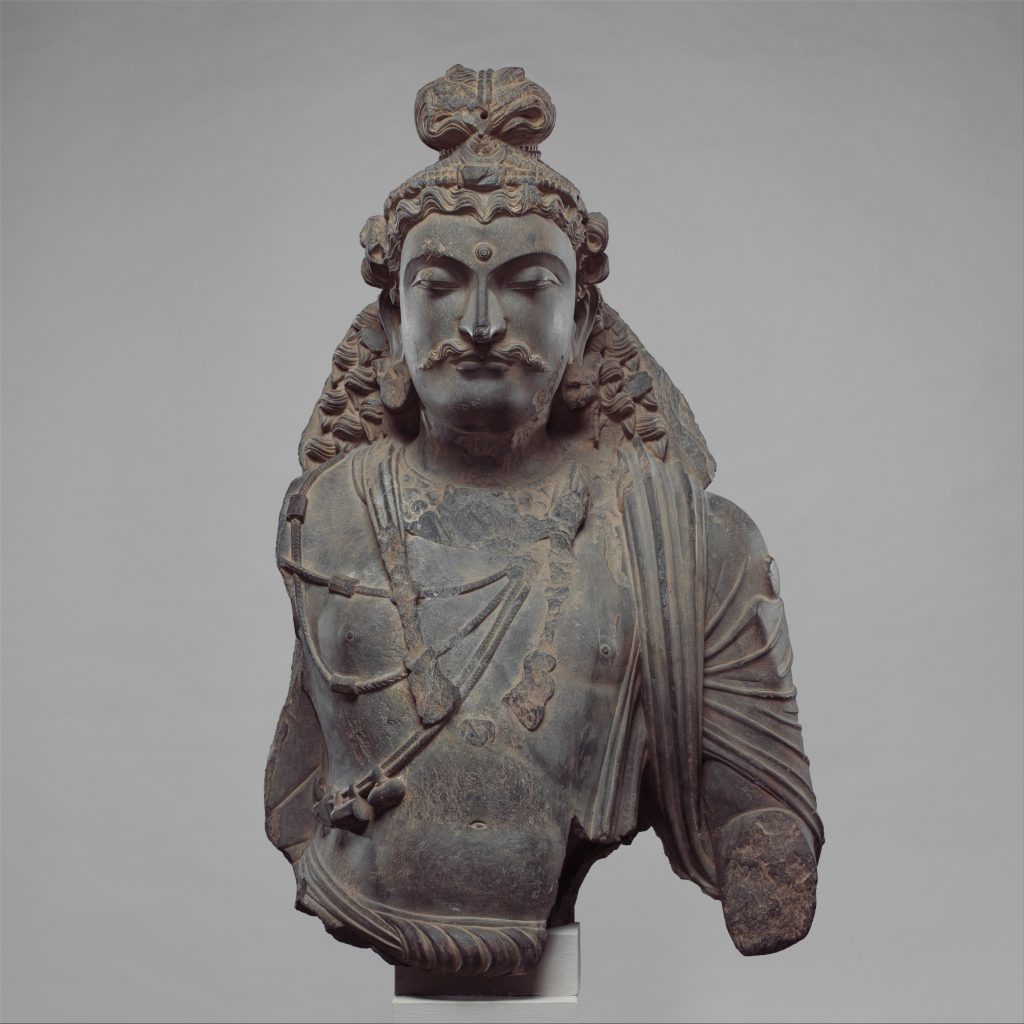
Gandhara ត្រូវបានអ្នកស្រាវជ្រាវជាច្រើនហៅថា ជាសាលានៃសិល្បៈ (Gandhara School of Art) ឬ ហៅបានថាអរិយធម៌ក្រិចរួមនឹងឥណ្ឌា។ Gandharaគឺជាតំបន់នៃសាសនា សិល្បៈ រវាងក្រិច និងឥណ្ឌា ហើយក៏ជាមជ្ឈមណ្ឌលពាណិជ្ជកម្មដ៏រីកចម្រើនតាមបណ្តោយផ្លូវសូត្រដែលតភ្ជាប់ប្រទេសចិន អាស៊ីខាងត្បូង និងមេឌីទែរ៉ាណេ។ នៅក្នុងប្រវត្តិសាស្រ្តនៃអរិយធម៌ Gandhara ឃើញមានការឈ្លានពានពីសំណាកអាណាចក្រផ្សេងៗជាច្រើនរួមមាន ក្រិច ផាធៀន គូសាន និង ពែក្ស ជាដើម។ យើងដឹងហើយថា ព្រះពុទ្ឋសាសនា គឺកើតឡើងនៅខាងជើងប្រទេសឥណ្ឌារហូតដល់តំបន់ Gandhara ប៉ុន្តែសិល្បៈដែលបង្ហាញអំពីការគោរពដល់ព្រះពុទ្ឋសាសនា (symbolic of Buddha) ក្នុងពេលនោះ គឺគោរពដល់ រូបដើមពោធិ៍ កងច័ក្រ និងរូបចេតិយជាដើម ប៉ុន្តែពុំទាន់ឃើញមានឆ្លាក់ ជារូបមនុស្សឡើងនោះទេ។ ការលេចឡើងដំបូងបំផុតនូវរូបព្រះពុទ្ធជាទម្រង់មនុស្សដែលហៅថា Buddha historic គឺស្ថិតនៅក្នុងសិល្បៈ Gandhara នេះហើយដែលអ្នកស្រាវជាវបានហៅ Gandhara ថាជាសាលានៃសិល្បៈ។ បើយើងសង្កេតលើទម្រង់ព្រះភក្រ្តនៃរូបព្រះពុទ្ធក្នុងអរិយធម៌នេះ គឺសឹងតែដូចទៅនឹងទម្រង់មុខពួកក្រិចដែលហៅថា Greco-Buddhist។ ភាគច្រើននៃពុទ្ធរូបក្នុងសិល្បៈ Gandhara គឺទម្រង់ព្រះពោធិសត្វ ក្នុងនិកាយមហាយាន។ សិល្បៈទាំងនោះបានអភិវឌ្ឍខ្លាំងនៅក្នុងសម័យកាល គូសាន។


ប្រភព៖ https://www.metmuseum.org
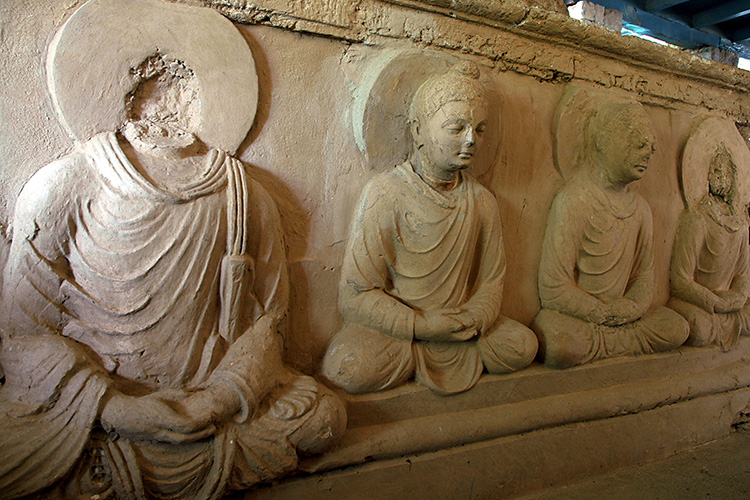
តាក់ស៊ីឡា (Taxila) ត្រូវបានគេស្គាល់ថាជាទីក្រុង និងមជ្ឈមណ្ឌលព្រះពុទ្ឋសាសនាដ៏ធំនៅក្នុងសម័យ Gandhara។ បច្ចុប្បន្នទីក្រុងនេះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងខេត្ត Punjab ប្រទេសប៉ាគីស្ថាន ហើយក៏បានចុះបញ្ជីក្នុងបេតិកភណ្ឌពិភពលោកដែរ។ នៅទីក្រុងនេះឃើញមានសំណង់ព្រះពុទ្ធសាសនាជាច្រើនរួមមានដូចជា ព្រះវិហារ ចេតិយ និងពុទ្ធបដិមាផ្សេងៗដែលសល់តាំងពីសម័យ Gandhara។

ប្រភព៖ www.news.cgtn.com
រាល់ព័ត៌មានដែលបានរៀបរាប់ខាងលើ គឺបង្ហាញថារដ្ឋនៃអរិយធម៌នេះចាប់មានឥទ្ធិពលនៅពាក់កណ្តាលស.វ.ទី៥មុនគ.ស. រហូតដល់ស.វ.ទី២ នៃគ.ស.។ សិល្បៈ នៃអរិយធម៌ Gandhara នេះហើយដែលបង្ហាញរូបព្រះពុទ្ធជាទម្រង់មនុស្ស ដែលយើងបានឃើញពុទ្ធបដិមាទាំងនោះនៅក្នុងទីក្រុង តាក់ស៊ីឡា និងនៅតាមសាមន្ទីរល្បីផ្សេងៗ។ ពុទ្ធបដិមាជាច្រើនៗត្រូវបាននាំចេញពីតំបន់ Gandhara ទៅបណ្តាសារមន្ទីរនៅបរទេសផ្សេងៗ ជាពិសេស នៅសារមន្ទីរ ហ្គីមេ (Guimet) ក្នុងប្រទេសបារាំង ប្រមាណជាង ២០០រូប ក្នុងនោះក៏មានយកពីទីក្រុង តាក់ស៊ីឡា និងនៅសារមន្ទីរ The Metropolitan Museum of Art នៅសហរដ្ឋអាមេរិកជាដើម។ រូបទាំងនោះត្រូវបានដាក់តាំងបង្ហាញរហូតដល់សព្វថ្ងៃនេះ៕
——————————-
Gandhara Civilization
Gandhara is the name of a famous ancient state and civilization that is now located in the northwest of Pakistan and Afghanistan, bordering on the west by the Gru Mountains and on the north by the foothills of the Himalayas. Based on the architecture, archeological remains, and especially Gandhara artifacts with the date more than 2,000 years.
Gandhara was a Buddhist devotion, but later in 330 BC. Alexander the Great covered the Gandhara region, and the influence of Greek civilization permeated the region which formed art and culture called Greco-Buddhist or Indo-Greek (Greek Buddhism).
Gandhara is called by many scholars the Gandhara School of Art, or Greek and Indian civilization. Gandhara is a region of religion, art between Greece and India, and a thriving commercial center along the Silk Road connecting China, South Asia, and the Mediterranean. In the history of the Gandhara civilization, there were invasions from many kingdoms, including Greece, Parthian, Kushan, and Persia. We realize that Buddhism originated in northern India as far as the Gandhara region, but the symbolic art of the Buddha at that time was to worship the Pipal tree, chakra, and the stupas but there were no human carvings have been found. The earliest appearance of the Buddha in human form, called Buddha historic, is in the Gandhara art, which researchers call Gandhara the School of Art. If we look at the form of the Buddha in this civilization, it is almost identical to the Greek form called Greco-Buddhist. Most of the Buddha images in Gandhara art are bodhisattva forms in the Mahayana sect. Those arts developed greatly during the Kushan period.
Taxila was known as a major Buddhist city and center in the Gandhara period. The city is currently located in Punjab province, Pakistan, and is a World Heritage Site. The city has many Buddhist structures, including churches, stupas, and other statues from the Gandhara period.
All the information mentioned above shows that the state of this civilization began to influence in the middle of the 5th century BC. Until the 2nd century AD. It is this art of Gandhara civilization that depicts the Buddha in human form, which we have seen in Taksila and other famous museums. Many of the Buddha statues have been exported from Gandhara to various museums abroad, especially at the Guimet Museum in France, with more than 200 statues, including those from Taxila and The Metropolitan Museum of Art in the United States and so on. Those statues are still on display today.
អត្ថបទដើម៖ លោក អេង តុលា






