សេន អាហ្គូស្ទីន (San Agustin) មានទីតាំងស្ថិតនៅខាងត្បូងនៃជួរភ្នំ អង់ដេស(Andes) និងស្ថិតនៅតំបន់ផ្នែកខាងលើនៃទន្លេ Magdalena ក្នុងខេត្ត ហ៊ូឡា (Huila) ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី ។ តំបន់នៃស្ថានីយនេះ គឺមានវិសាលភាពទឹកដីធំធេងដែលផ្ទៃដីខាងលិចចាប់ពី តំបន់ព្រៃទឹកភ្លៀង Chocoan រហូតដល់សមុទ្រប៉ាស៊ីហ្វិច។
លើសពីនេះសេន អាហ្គូស្ទីន គឺជាទីតាំងនៃសាសនាដ៏ធំរបស់ប្រជាជនបុរាណក្នុងតំបន់ទ្វីបអាមេរិកខាងត្បូង ក្នុងចំណោមបណ្តាវប្បធម៌ដទៃទៀតក្នុងទ្វីបអាមេរិកដូចជា ឆាវិន, អូមិច, មីយ៉ា ជាដើម។ ស្ថានីយបុរាណវិទ្យាមួយនេះក៏បានចុះក្នុងបញ្ជីបេតិកភណ្ឌពិភពលោកក្នុងឆ្នាំ១៩៩៥។
ប្រភព៖ UNESCO
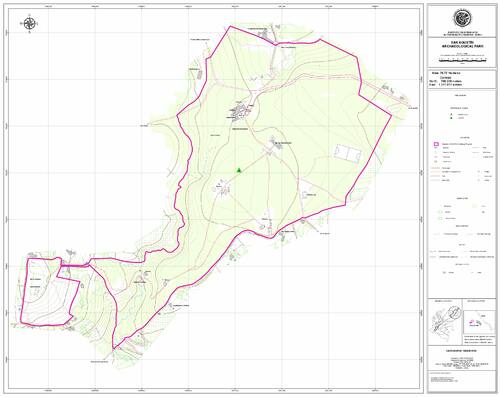
ការងារស្រាវជ្រាក្នុងតំបន់ សេន អាហ្គូស្ទីនបានចាប់ផ្តើមឡើងដំបូងក្នុងឆ្នាំ១៩៦០ រហូតដល់ឆ្នាំ ១៩៧៥ ដែលក្នុងអំឡុងពេលនោះ ការស្រាវជ្រាវសំខាន់ៗ គឺជួសជុល និងរៀបចំសំណង់ក្នុងស្ថានីយសេន អាហ្គូស្ទីនឡើងវិញ ដោយសារសំណង់ភាគច្រើនត្រូវបានចោរលួច គាស់កកាយ បំផ្លាញ។ នៅឆ្នាំ១៩៦៤ អ្នកបុរាណវិទូជនជាតិកូឡុំប៊ីម្នាក់ឈ្មោះ Duque Gómez បានបោះពុម្ពសៀវភៅអំពីការងារស្រាវជ្រាវនៅក្នុងតំបន់នេះ ដោយលោកក៏បានបង្ហាញអំពីកាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃស្ថានីយនេះដែលមានស្រទាប់ដីចាស់ជាងគេក្នុងឆ្នាំ៣៣០០មុនគ.ស.។ គួរបញ្ជាក់ដែរថាតំបន់នេះក៏ជាបណ្តុំនៃសំណង់សាសនាដ៏ធំក្នុងទ្វីបអាមេរិកខាងត្បូងដែលមានរូបរាងរហូតដល់សព្វថ្ងៃនេះ។
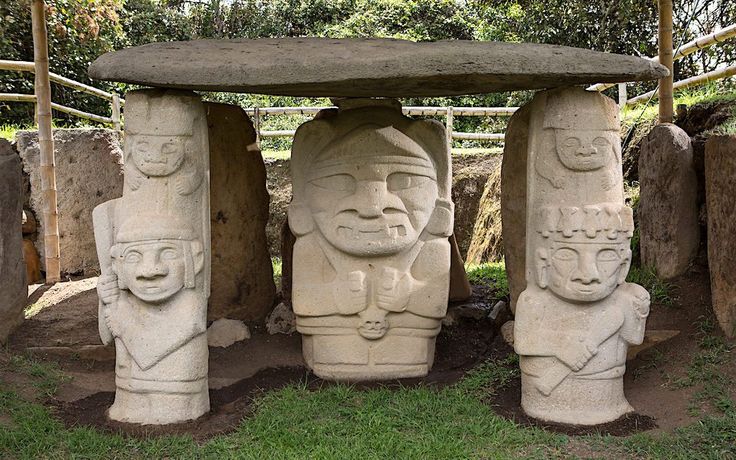
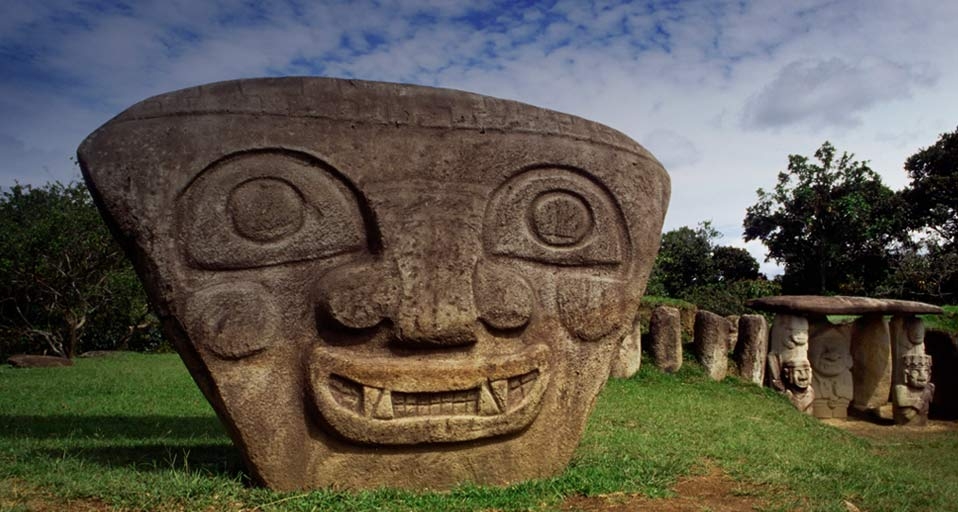
សំណង់នៅក្នុងស្ថានីយបុរាណវិទ្យាសេន អាហ្គូស្ទីនគឺជាបណ្តុំនៃសំណង់ស្ថាបត្យកម្មបែបសាសនា ដូចជា សំណង់សម្រាប់បញ្ចុះសព ប្រាសាទ និង ទីតាំងសំណង់សាសនា ផ្សេងៗទៀត ដែលកសាងជាពន្នូកដីនិងមានថ្ម។ បច្ចុប្បន្នស្ថានីយនេះមានផ្ទៃដី១១៦ហិតាដែលបែងចែកជាបីតំបន់គឺ Mesita A, Mesita B, Mesita C។ ទីតាំងនៃសំណង់ទាំងនោះគឺស្ថិតនៅក្បែរៗគ្នា មានគម្លៀតពីមួយទៅមួយប្រមាណជាង៣០ម និងមានផ្លូវធំមួយនៅខាងមុខ។ ចំពោះសំណង់ផ្នូរដែលកសាងអំពីថ្មធំ កសាងនៅក្នុងសម័យកាលដំបូង(១ដល់៩០០នៃគ.ស.) ដែលសម្រាប់មេដឹកនាំធំក្នុងសម័យកាលនោះ។
តាមរយៈសំណង់ស្ថាបត្យកម្មទាំងនោះ ទីតាំងនៃស្ថានីយនេះគឺជាទីក្រុងនៃសាសនាដ៏ធំរបស់មនុស្សសម័យបុរាណក្នុងប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី និងក្នុងទ្វីបអាមេរិកខាងត្បូងផងដែរ។ រូបចម្លាក់ដែលឃើញមាននៅទីនេះ គឺស្រដៀងទៅនឹងរូបនៅតំបន់ភ្នំអង់ដេស ខាងជើង ដែលស្ថិតនៅក្នុងទ្វីបអាមេរិកកណ្តាល។ សិល្បៈសំណង់ស្ថាបត្យកម្មក្នុងស្ថានីយ សេន អាហ្គូស្ទីន គឺមានភាពប្លែក និងមានតែមួយ ដែលបានបង្ហាញអំពីបច្ចេកទេស និងគំនិតច្នៃប្រឌិតអំពីការកសាងផ្នូរ និងការឆ្លាក់រូបចម្លាក់សម្រាប់ឧទ្ទិសដល់ទេព។ តាមរយៈទីតាំងភូមិសាស្រ្ត អ្នកស្រាវជ្រាវលើកឡើងថា ប្រជាជនក្នុងតំបន់នេះរស់នៅក្នុងព្រៃទ្រូពិកដែលពឹងលើការបរបាញ់សត្វ ព្រៃ និងនេសាទ។ ក្រៅពីនេះ តំបន់នៃស្ថានីយនេះត្រូវបានបោះបង់ចោលប្រហែលនៅឆ្នាំ១៣៥០នៃគ.ស. និងមានការមកតាំងទីវិញនៅស.វ.ទី ១៨ និង ១៩នៃគ.ស.។

ប្រភព៖ UNESCO

ប្រភព៖ UNESCO

ប្រភព៖ UNESCO
ការសនិ្នដ្នានដោយអ្នកស្រាវជ្រាវបុរាណវិទ្យាការបោះបង់ចោលនោះ គឺប្រហែលមកពីកត្តាធម្មជាតិដែលមានការរញ្ជួយដី និងប្រហែលពីការឈ្លានពានពីអរិយធម៌ផ្សេងនៅក្នុងទ្វីបអាមេរិកជាពិសេស អេស្បាញ និងព័រទុលហ្គាល។ ក្រុមអ្នកស្រាវជ្រាវបានបន្តការងារជួសជុលរូបចម្លាក់ និងជួសជុលផ្នូរនៅក្នុងទីតាំងនោះ ដើម្បីបើកបង្ហាញសាធារណៈជនឲ្យបានចូលទស្សនាផងដែរ៕
——————————
San Agustin Cultural site
San Agustin is located south of the Andes Mountains and in the upper reaches of the Magdalena River in Huila province, Colombia. The area of this site is vast, extending westward from the Chocoan rainforest to the Pacific Ocean. In addition, San Agustin was the site of the great religion of the ancient peoples of South America, among other cultures in the Americas, such as Chavin, Omix, and Mia. This archeological site was also designated on the World Heritage List in 1995. The first research in the San Agustin area was conducted from 1960 until 1975, which was carried out on the restoration and reconstruction San Agustin site, as most of the structures were looted and destroyed. In 1964, a Colombian archaeologist, Duque Gómez, published a book on research work in the area, showing the date of the site with the oldest soil layer in 3300 BC. It should be noted that this area is also a large religious buildings complex in South America that has been used until today.
The buildings in the San Augustin Archaeological Site are a collection of religious architectural structures, such as cemeteries, temples, and other religious sites built of soil and stone. Currently, the site covers an area of 116 hectares, which is divided into three areas: Mesita A, Mesita B, and Mesita C. The locations of these buildings are close to each other, with a spacing of more than 30 meters and the main road in front. As for the tombs built of large stones were built in the early period (1 to 900 AD), which was for the great leaders of that period.
According to these architectural structures, the location of the site was the largest religious city of ancient peoples in Colombia and in South America as well. The sculptures seen here are similar to those in the North Andes Mountains in Central America. The architectural art in San Augustin is unique and exemplary, showcasing the techniques and innovations of tomb construction and sculpture dedicated to the gods. In addition, based on the geographical location, the researchers stated that the people in this area live in tropical forest, which depends on hunting and fishing. In addition, the area of this site was abandoned around 1350 CE and was repatriated in the 18th and 19th centuries CE.
In conclusion, the archaeologists have speculated that the abandonment may have been due to natural factors such as earthquakes and invasions from other civilizations in the Americas, especially Spain and Portugal. Researchers have continued to repair statues and graves in the area to open them for public visiting.
អត្ថបទដោយ៖ លោក អេង តុលា






